Lime Kiln Technology
By Jorge L. Lerena
1. Selecting the Proper Lime Kiln Technology
Lime is a key industrial mineral many industries use as a chemical additive. The industrial facilities that utilize Lime in various forms are metal ore processing, metallurgy, steel, paper, pharmaceuticals, sulfur removal, and water treatment. It is also used to generate many basic chemicals used to manufacture consumer goods.
Lime is produced through the calcination of carbonate minerals, calcium, and magnesium in Rotary Kilns or Vertical Kilns. The main types of Lime Kilns are:
1.1. Long Rotary Kilns
The main advantages of long rotary kilns are:
- Large production volumes.
- Wide range of feed sizes.
- Medium to high reactivity Lime.
- Low sulfur Lime.
- Flexibility in fuels used.
- Production not affected by limestone decrepitation.
- Can use high-sulfur coal and pet coke.
The main disadvantages of long rotary kilns are:
- High CAPEX.
- Highest OPEX (high energy usage).
- A contact cooler may not be applicable if the product is very fine.
Figure 1. Long Rotary Kiln

1.2. Preheater Rotary Kilns
The main advantages of preheater rotary kilns are:
- Large production volumes.
- Wide range of Limestone feed sizes.
- Medium to high reactivity Lime.
- Fuel flexibility.
The main disadvantages of preheater rotary kilns are:
- Limestone decrepitation can cause “plugging” in the preheater.
- High CapEx.
- OpEx higher then shaft kiln.
- Low fuel efficiency of rotary kilns.
- Cannot use high sulfur coal and pet coke for steel customers.
Figure 2. Preheater Rotary Kiln
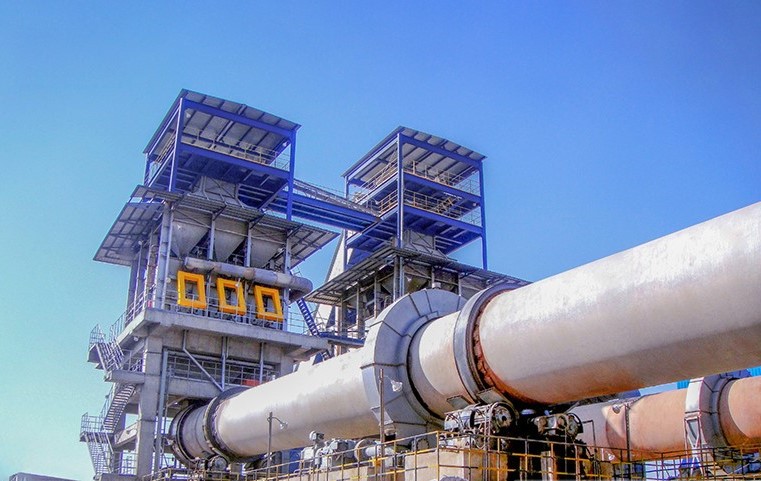

1.3. Single-Shaft Vertical Kilns
The main advantages of single-shaft vertical kilns are:
- Low CAPEX.
- Short Schedule.
- Competitive fuel efficiency.
The main disadvantages of single-shaft vertical kilns are:
- Low production volumes.
- Will not work if Limestone decrepitates.
- Limited Limestone feed range.
- Low Lime reactivity.
Figure 3. Single-Shaft Vertical Kiln

1.4. Annular Shaft Kilns
The main advantages of annular shaft vertical kilns are:
- High concentration of CO2 in off-gas for use in further chemical processes.
- Good fuel efficiency
- No need to wash limestone feed.
- Capable of adjusting Lime reactivity production levels.
- Effective in producing. dead-burned lime
The main disadvantages of annular shaft vertical kilns are:
- Limited production volumes.
- Will not work if Limestone decrepitates.
- Limited Limestone feed range.
- Limited Lime reactivity.
Figure 4. Annular Shaft Kiln
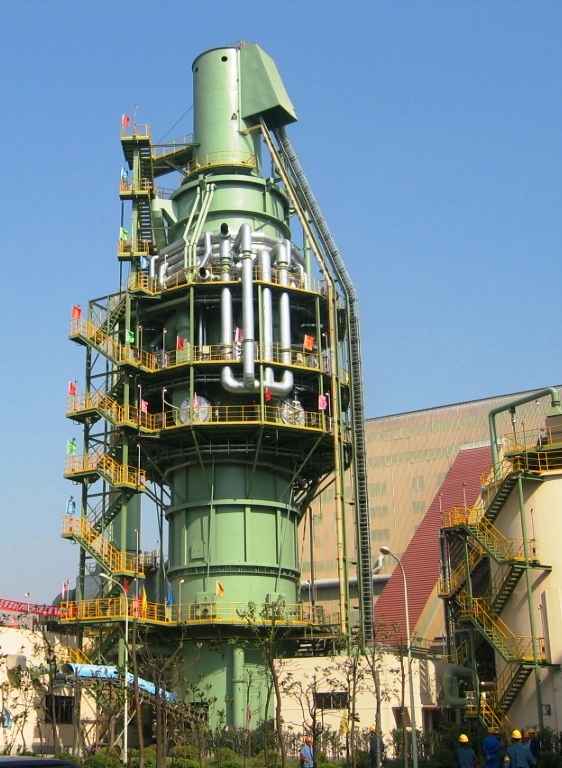

1.5. Parallel Flow Vertical Shaft Kilns
The main advantages of parallel flow vertical shaft kilns are:
- Best fuel efficiency of all Lime Kilns.
- Capable of producing medium to very high reactivity Lime.
The main disadvantages of parallel flow vertical shaft kilns are:
- Will not work if Limestone decrepitates.
- Limited range of feed sizes.
Figure 5. Parallel Flow Vertical Shaft Kiln
The decision on the technology to be used is based on many factors, including the desired product characteristics, limitations of the geographical area, fuel properties and cost, etc. Some of the most important aspects to be considered are:
- Market (Lime use): Lime reactivity (low, medium, or high) and sulfur contents are common specifications that depend directly on the technology used.
- Availability of Limestone resources and industry capability to manage large amounts of fines: Rotary kilns allow kiln feed size variations. This allows utilizing the smaller stone particles (down to ¼” [6mm]) generated in mining, crushing, and screening, hence increasing the mine’s life.
- Physical Properties of the Limestone and Lime: Although the fuel efficiency of vertical kilns is much higher than that of rotary kilns, limestone could break down into smaller pieces during calcination due to the “decrepitation” phenomenon which clogs vertical kilns, making the process not feasible. Likewise, the lime created during the calcination process should have sufficient physical strength to carry the weight of the limestone bed in the kiln.
2. Lime Industry – PEC Consulting’s Active Participation
PEC Consulting Group has provided technical assistance to industries and processing facilities that benefit from the use of lime. In doing so, we have actively helped industries meet the ever increasing demand for the production of quality lime. Sample Scopes of Work have included:
- Feasibility and Technical Studies for Greenfield lime production facilities.
- Technical Studies for capacity increase of existing plants.
- Investigation of potential raw material deposits such as sea shells, travertine, and limestone.
- Geological exploration, core drilling programs, and testing for raw material physical and chemical properties.
- Mining Plans.
- Conceptual design of mine and plant.
- Flow sheets, layouts, equipment lists, and basic designs. Basic equipment specifications. Technology comparisons of major process equipment tenders.
- Capital cost and operating cost estimates.
- Logistics for supplying the mine facilities.
- Economic viability analysis of the projects.
A study forms the foundation for future development and it is an absolute necessity for successfully carrying a project to completion. By delivering a well-prepared and thorough study, PEC Consulting Group helps its clients achieve their desired goals and competitive edge.
About the Author(s)
Jorge L. Lerena
Mr. Lerena has over 15 years of experience in project management and design as well as financial and economic valuation of Cement and Lime Plants. He has internationally proven planning, coordination, negotiation, and managing skills. His expertise also includes the evaluation of limestone reserves and studies for the expansion of Brownfield lime plants and for Greenfield lime plants in South America, including geological evaluations and process selection. Mr. Lerena achieved an Executive MBA from ESEUNE “Escuela Europea de Estudios Universitarios y de Negocios” in Bilbao, Spain. He earned a BS in Industrial and Systems Engineering from the Universidad de Piura, Peru.
PEC Consulting Group LLC | PENTA Engineering Corporation | St. Louis, Missouri, USA
How can we help you? Get in touch with our team of experts.
